As we approach the end of the year, the global climate pattern often changes due to natural cycles like La Nina. La Nina is a naturally occurring global climate pattern, which can cause extreme weather across the planet. The effect of the same might vary from place to place. La Nina is a cool phase of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation.
La Nina: Duration & Effects
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Climate Prediction Center, there is a 60% chance that a weak La Nina event will develop this autumn i.e., December 2024 and could last until early spring i.e., March 2025.
Although it is not known how this La Nina will develop, there are some common trends. Experts believe that…
1. Higher than usual rainfall
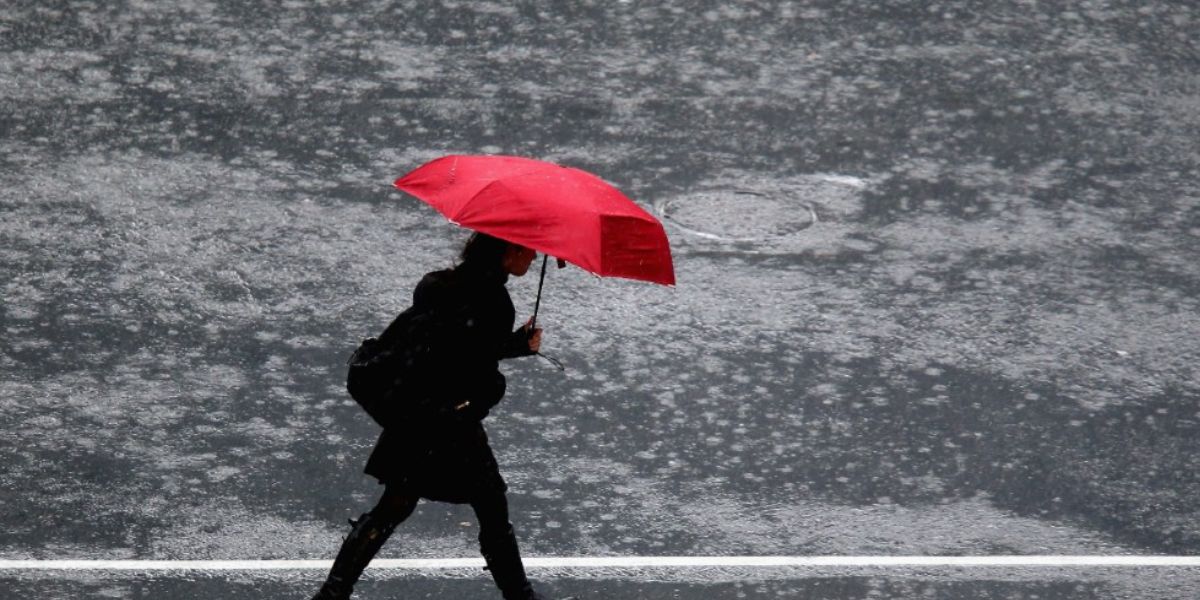
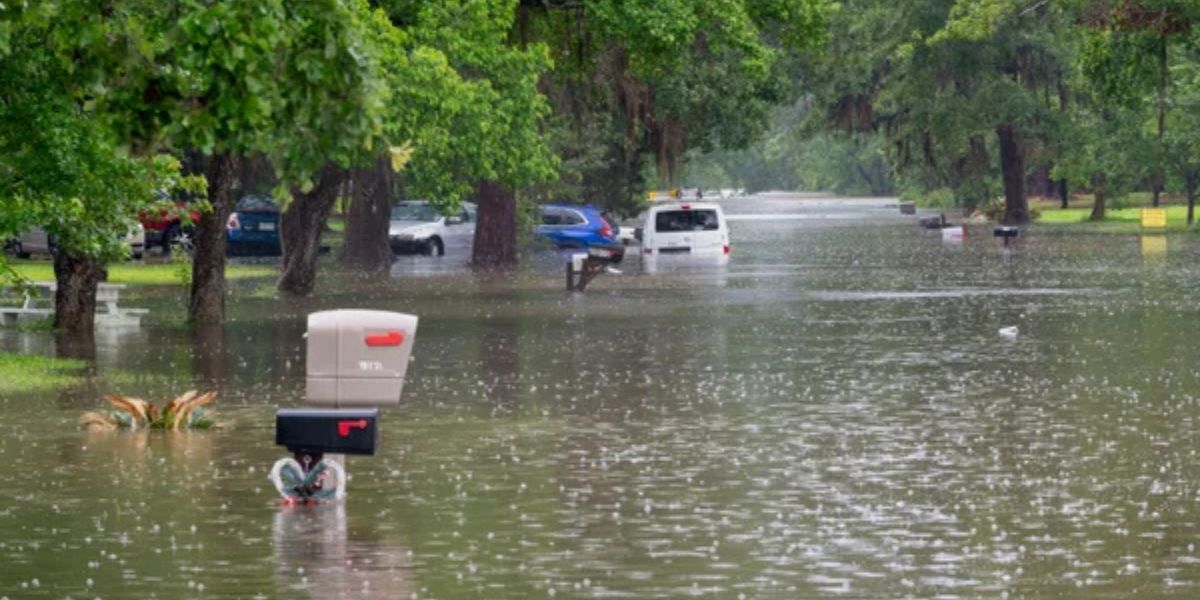
Rainfall may be higher than usual in Northern parts of South America- Ohio Valley, the Great Lakes area, and the Northwest.
2. Drier than normal places
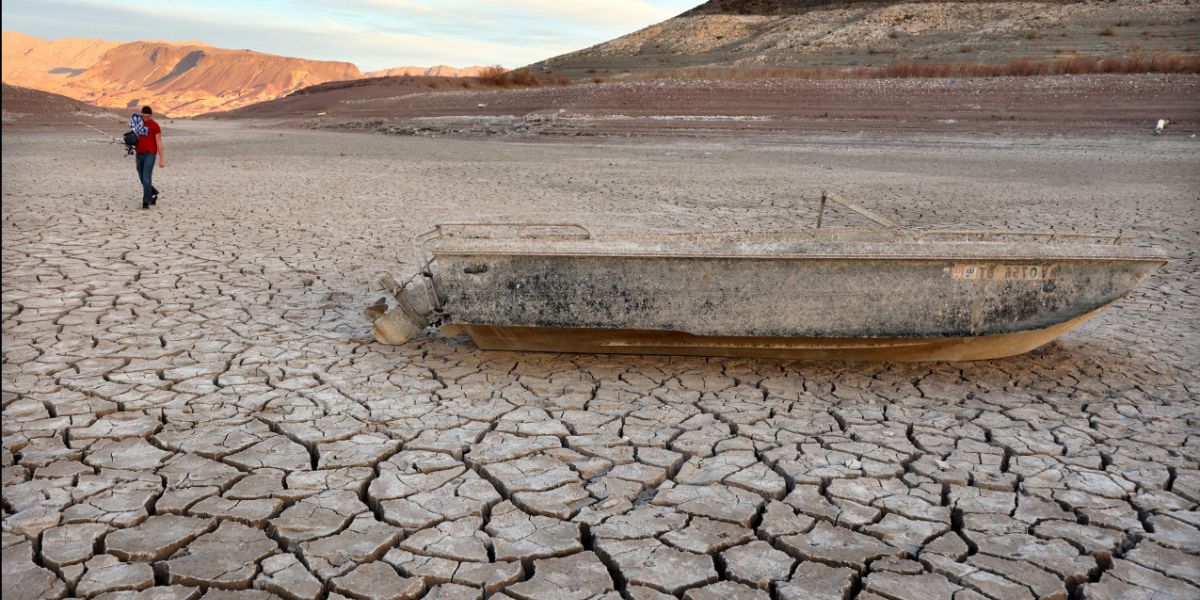
Southern parts of the US and some areas of Mexico- the southwestern part of Colorado, the southeastern part of Utah, the northeastern part of Arizona and the northwestern part of New Mexico and into the Southeast, might could be drier than normal.
3. Wetter-than-average conditions
The northern U.S. and southern Canada may experience wetter-than-average conditions.
4. Forecast doesn’t provide snowfall prediction
Since the snow forecasts are typically inaccurate more than a week ahead, the forecast does not provide snowfall predictions.
5 Warmer-than-average temperatures
Expect warmer-than-average temperatures in the southern U.S. to the eastern Great Lakes, the eastern seaboard, New England and northern Alaska.
6. Drought situations might improve or end
In Ohio River Valley, the Great Lakes region and parts of the northwestern U.S., such as eastern Washington, Oregon, and northern and central Idaho, drought conditions might improve or possibly come to an end.
7. Above-average precipitation
Expect above-average precipitation in northern and western Alaska, the Pacific Northwest, and the northern U.S., especially in parts of Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky.
8. Drier than usual & drought conditions

9. Seasonal total precipitation
There is equal chances of below-average, average or above-average seasonal total precipitation in most parts of California, the central Plains states and the area along Interstate 95 from Boston to Washington, D.C.
10. La Nina affects weather based on location & season
The climate scientist at NOAA, Michelle L’Heureux mentioned that La Nina affects weather differently based on location as well as the season. Parts of South America, such as eastern Argentina, may experience drier conditions. Also, places like northern Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela may be wetter than usual.
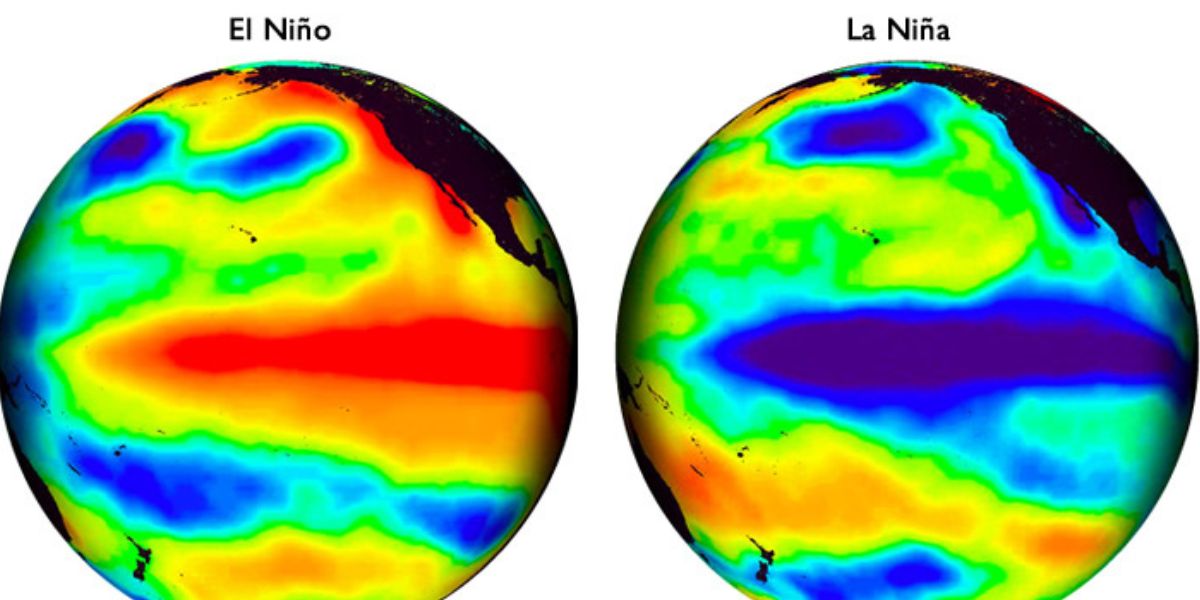
Difference between La Nina & El Nino. What happens during La Nina?
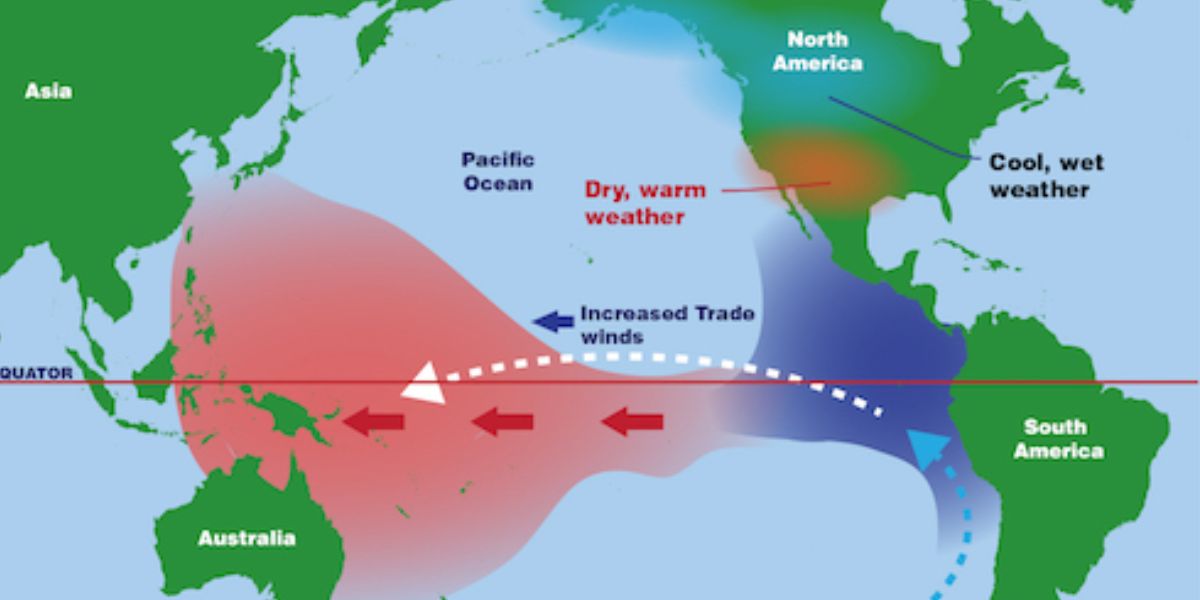
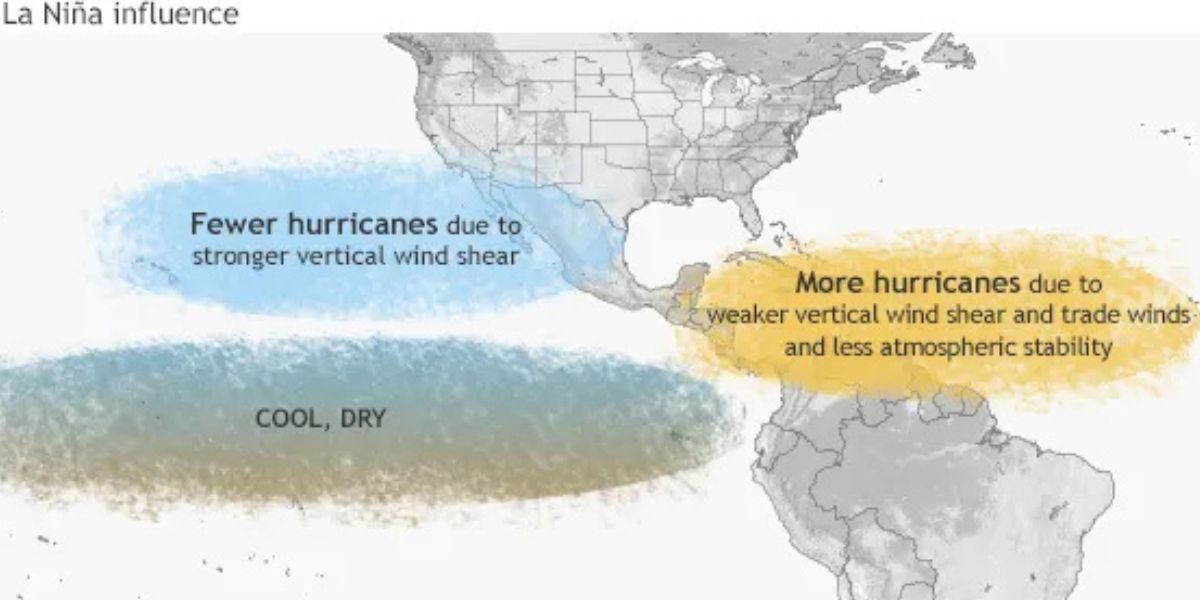
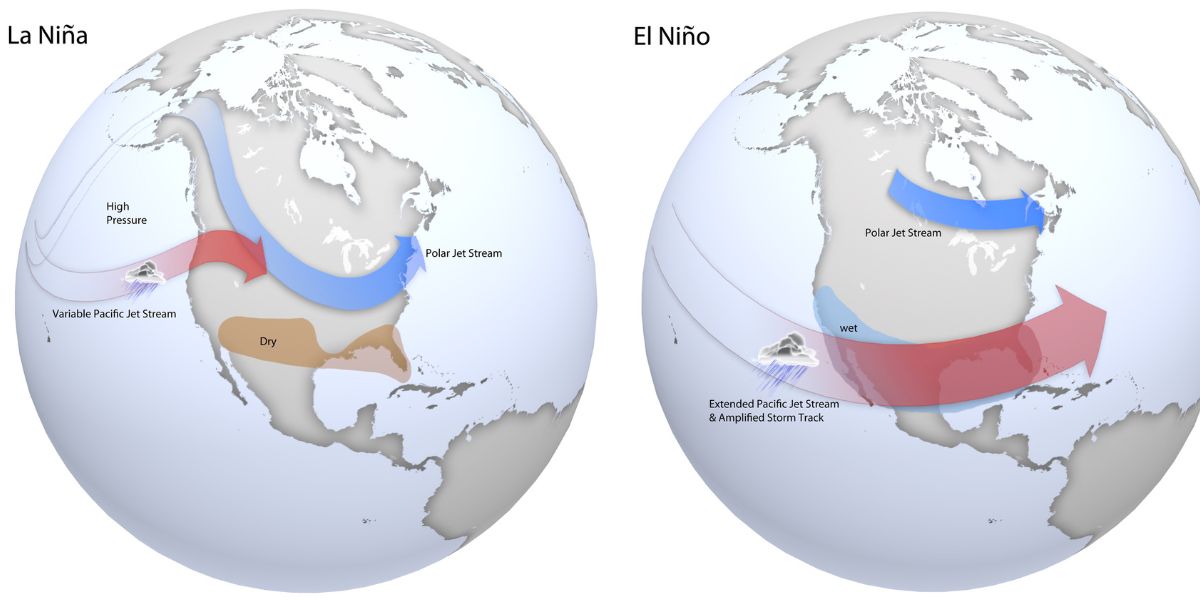
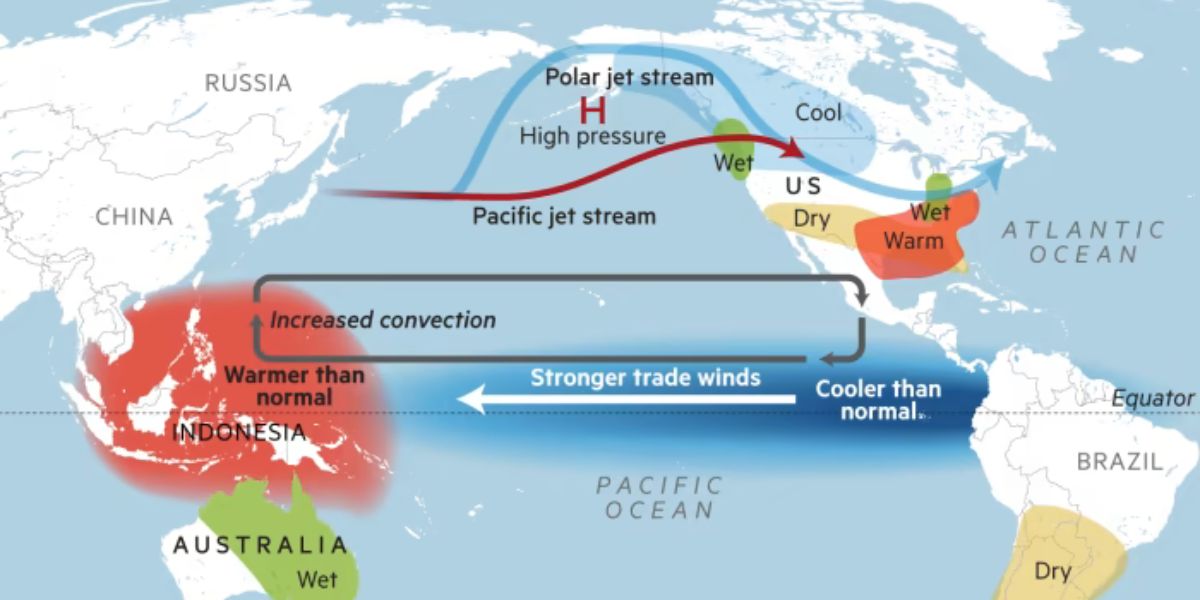
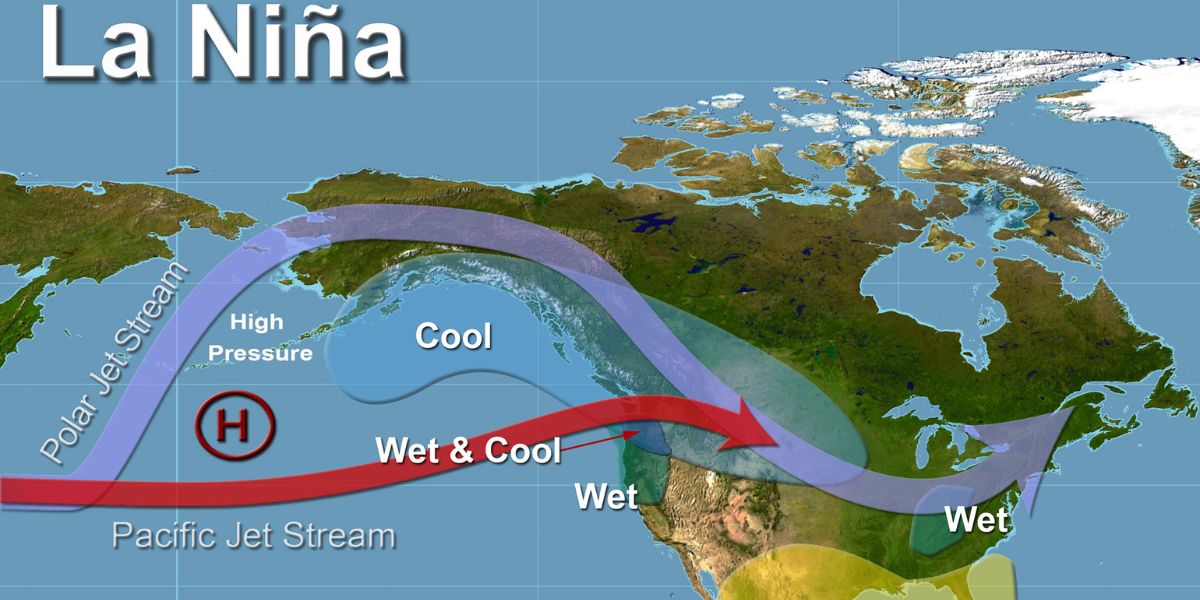
This phase cause shifts in wind and ocean temperatures in the Pacific, which can result in extreme weather worldwide. While El Nino is a warm phase and occurs when trade winds, which usually blow across the Pacific Ocean towards Asia weaken. As a result, warm water accumulates along the western coast of South America. On the other hand, in La Nina, stronger trade winds cause colder water from the deep ocean rises to rise to the surface, because of which ocean temperature in the eastern Pacific becomes much cooler than usual, and this in turn affects the jet stream’s path. During La Nina, the jet stream move northward and as it travels over ocean, it picks moisture, which affect the path of storms and boost precipitation.
Triple-dip La Nina event
Recently, the earth experienced a rare “triple-dip” La Niña event, i.e., we had back-to-back three winters with La Nina conditions from 2020-2023. It’s rare because the previously one was in 1973 to 1976. A climate scientist at NOAA, Michelle L’Heureux, mentioned that La Nina events tend to last longer and happen more often than El Nino events.
Frequency of La Nina can impact specific places
Commenting on the forecast of La Nina this year, another climate scientist Ben Cook said that although it is unusual, it is not unpredicted. He mentioned that frequency of La Nina events can be stressful for regions (like East Africa) that are already experiencing drought. If another La Nina event occurs, then the drought conditions might continue, making it difficult for the affected areas to recover.
Connection between climate change, La Nino and El Nino
The connection between climate change and the La Nina and El Nino is not fully clear. A climate scientist at the University at Albany, Paul Roundy explains that climate models suggest that El Nino events may become more frequent and there might be fewer La Nino events, but not all models agree with this. It’s because computer models also find it difficult to distinguish between normal changes in these phases and the effects of climate change. Roundy mentioned that while now we are getting to see multiple La Nina events, but, may be in 40-50 years, it might just be an opposite pattern, as nature has its own variation.